Study Notes
Subsidies - 2021 Revision Update
- Level:
- AS, A-Level, IB
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB, Eduqas, WJEC
Last updated 7 Jan 2021
In this revision resource, we apply, analyse and evaluate government subsidies to producers and consumers in different markets.
A subsidy is any form of government support—financial or otherwise—offered to producers and (occasionally) consumers. Subsidies to producers reduce the marginal cost of supply.
A subsidy usually leads to an increase in the output sold of a good or service at a lower market price.

Examples of government subsidies to producers
- Job Retention Scheme (wage subsidy) for furloughed workers during the pandemic
- Government grants for businesses employing youth unemployed / long term jobless
- State aid for loss-making businesses such as airlines & train operating companies, bus companies and steel plants
- Subsidies for construction companies for example to build low-cost affordable housing
- Export subsidies for selected producers – where the government offers a minimum priced for selling products overseas
Examples of government subsidies for consumers
- Subsidies for people buying electric vehicles
- Feed-in tariffs for renewable energy fed back into the grid by households
- Food and energy subsidies – often used in emerging / developing countries
- Boiler scrappage schemes – a grant to help households to install newer, fuel-efficient heating systems
- Free television licences for the over-75s
- Scotland – new legal duty in 2021 on local authorities to ensure that free items such as tampons and sanitary pads are available to "anyone who needs them".
- Subsidies (tax-free) for childcare
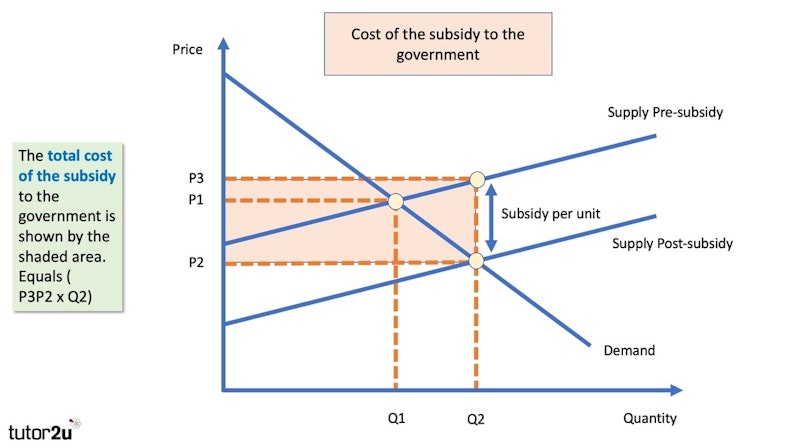
Subsidies - analysis diagrams
In this video we go step-by-step through how to show the effect of a government subsidy offered to suppliers using an analysis diagram.

Subsidies - Evaluation Perspectives
When might subsidies be justified as a government intervention in a market?
- Helping poorer families with food and childcare costs particularly during an economic crisis
- Improved nutrition can lift labour productivity and reduce the long-term burden on health services
- Encourage output and investment in fledgling sectors such as life sciences and renewable energy
- Protect jobs in loss-making industries hit by recession and by external economic shocks
- Improve housing and transport affordability to improve geographical mobility of labour
- Reduce the cost of training & employing workers
- Encourage the arts and other cultural services which have social benefits
What are some of the potential disadvantages of government subsidies?
- Producers can become “subsidy dependent”
- Subsidies can distort resource allocation
- Subsidies can lead to excess production / surpluses
- Environmental risks from excessive production
- Government failure arising from political lobbying
- Subsidies can be very expensive - taxpayers bear the cost
You might also like
Jamie Oliver calls for Sugar Tax on Soft Drinks
20th October 2015
Ban on online junk food ads for kids
8th December 2016

France makes childhood vaccinations compulsory
9th August 2017
Introduction to Supply Side Policies (Online Lesson)
Online Lessons
Maximum Prices - 2021 Revision Update
Study Notes