Study Notes
Patents
- Level:
- A-Level
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB
Last updated 22 Mar 2021
A patent provides a right under law to produce and market a good for a specified period of time
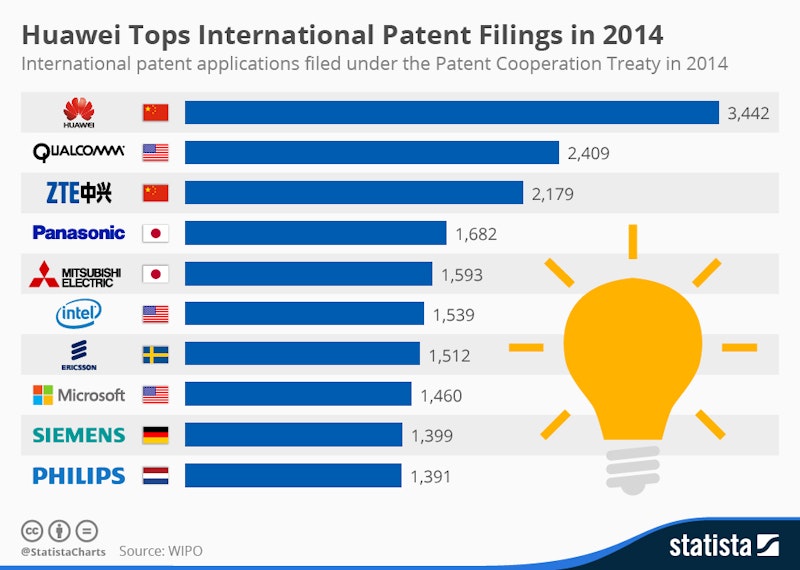
Benefits of patents for businesses:
- Helps to develop a competitive advantage via a unique feature
- Provides a source of monopoly power
- Barriers to entry maintain supernormal profits in the long run
- Enables firms to develop into a new market e.g. through a disruptive technology that has been patented
Justifying patent protection for the wider economy
- Encourages Research and Development
- Encourages exploitation of external economies of scale e.g. research projects with universities
- Innovation is encouraged e.g. gains in dynamic efficiency that then reduce costs for consumers
- Macro benefits, e.g. multiplier effects, gains in export competitiveness, a source of economic growth
- Investment in research in turn in the long run may benefit society as a whole e.g. external benefits from health research, environmental patented technology
Some counter-arguments on the effects of patents:
- Patents allow supernormal profits to be made – a transfer of wealth to highly profitable monopolists
- Patents may stifle competition or innovation by others
- Alternatives to patents might help stimulate research e.g. subsidies to university research
- Disadvantages of monopoly e.g. loss of allocative efficiency as prices charged are well above MC
- May cause x-inefficiency due to the lack of contestability in the market
- Costs of enforcing patents
You might also like
Supply-Side Economics - Research and Development
Study Notes

China cuts tariffs on imported consumer goods
26th May 2015
China should avoid an economic meltdown
18th October 2015

Chinese Economic Reform - An Overview
7th February 2016

Beyond the Bike Lesson Resource - Shenzhen's development
23rd May 2016

Globalisation - How Mexico is Becoming the New China
4th May 2023