Study Notes
Macroeconomic Objectives and Macro Stability
- Level:
- AS, A-Level
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB
Last updated 21 Mar 2021
In this blog we look at the main objectives of economic policy in the UK and other countries.
- Objectives are the goals of government policy
- Instruments are the means by which these aims might be achieved
For example, the government might want to achieve an objective of a low rate of price inflation. The main instrument to achieve this are changes in monetary policy interest rates, since 1997 they have been set by the Bank of England. Fiscal policy could be another instrument to achieve this aim. This is in the hands of the government. Supply-side policies can also be used to control inflation and promote growth over the longer-term.
The government might have another objective to make the distribution of income more equal. It would then choose the policy instruments it thinks are best suited to reaching to this aim, perhaps a change in the income tax system or a rise in the national minimum wage.
The main policy instruments available to meet macroeconomic objectives are
- Monetary policy –changes to interest rates, the supply of money and credit and also changes to the value of the exchange rate
- Fiscal policy – changes to government taxation, government spending and borrowing
- Supply-side policies designed to make markets work more efficiently
Objectives of UK Macroeconomic Policy
The key objectives for the UK are:
- Stable low inflation - the Government’s inflation target is 2.0% for the consumer price index.
- Sustainable growth – growth of real gross domestic product – sustainable in keeping inflation low and reducing the environmental impact of growth.
- Improvements in productivity – this is designed to improve competitiveness and global trade performance
- High employment - the government wants to achieve an increase employment and eventually a situation where all those able and available can find meaningful work
- Rising living standards and a fall in relative poverty – cutting child poverty and reducing pensioner poverty.
- Sound government finances - including control over state borrowing and the total national debt

Additional objectives of macroeconomic policy

What is meant by macroeconomic stability?
- Economic stability occurs when there is low volatility in key indicators such as prices, jobs, economic growth, interest rates, investment and trade.
- All countries experience an economic cycle which tracks the fluctuations in the rate of growth of a country’s Gross Domestic Product, some countries have a more volatile cycle than others
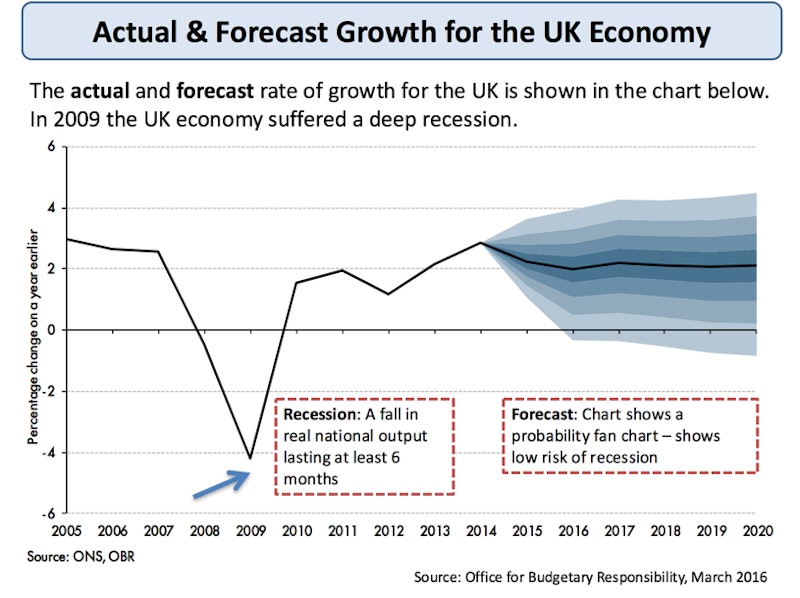
Macro stability is shown in particular by the volatility of a country's economic cycle. The chart below tracks the annual % change in real GDP for the UK economy including forecasts made at the time of the March 2016 Budget.
You might also like
Fiscal Policy - Government Intervention
Study Notes

FDI and LRAS: Microsoft to open UK data centres
10th November 2015
Household Saving and Aggregate Demand
Topic Videos

The Folly of Negative Interest Rates
13th September 2016

UK Economic Performance - "Dial up" activity
13th January 2018