Study Notes
Economic complexity and competitiveness
- Level:
- AS, A-Level, IB
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB, Eduqas, WJEC
Last updated 5 Feb 2019
Data on trade can provide important clues about the complexity and capability of different countries in the world economy.
Some countries continue to show a high level of primary product dependency where extractive industries such as crude oil, copper mining and farming account for a significant percentage of national output, employment and exports. Many of these countries are vulnerable to changes in world prices which then impact on the terms of trade, the balance of trade and government tax revenues and fiscal balances.
Consider for example the commodity pattern of trade of a country such as Angola.
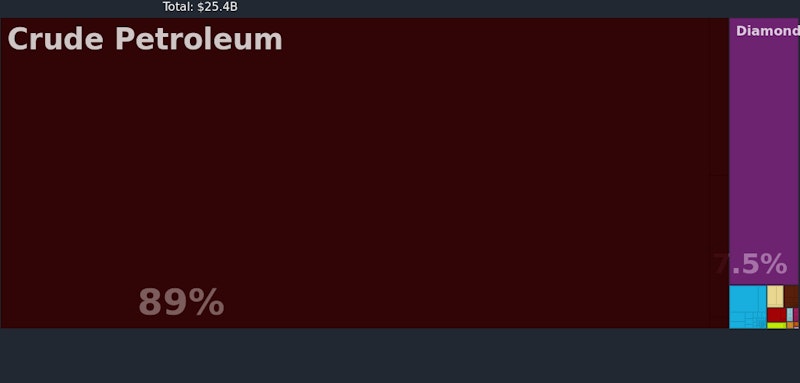
Other countries are developing a comparative and competitive advantage in light manufacturing such as textiles, helped by substantial inflows of foreign direct investment. A good example of this is Bangladesh. Textiles now employs over four million people, and whilst there is a lovely debate about the economic and social impact of TNC investment in these nations, increasing the flow of waged income from regular employment can be an effective pathway towards reducing extreme poverty.
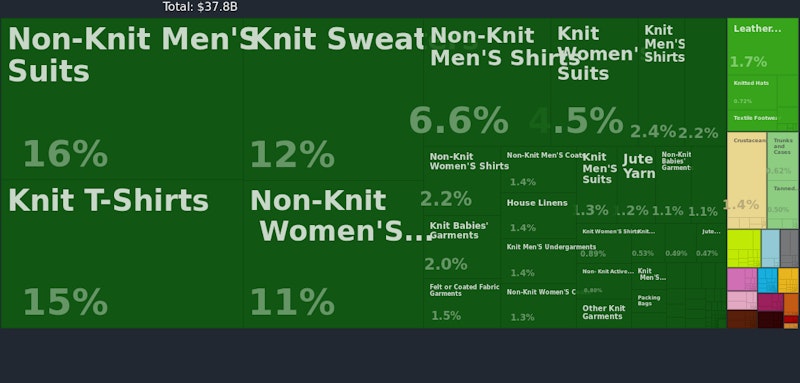
Vietnam is another country attracting sizeable foreign direct investment into labour intensive manufacturing industries. One of the big challenges for these countries is to use rising per capita incomes and investment as a catalyst for improving human capital. This is critical to expanding not just productive capacity (aka long run aggregate supply) but also the capabilities of the labour force.
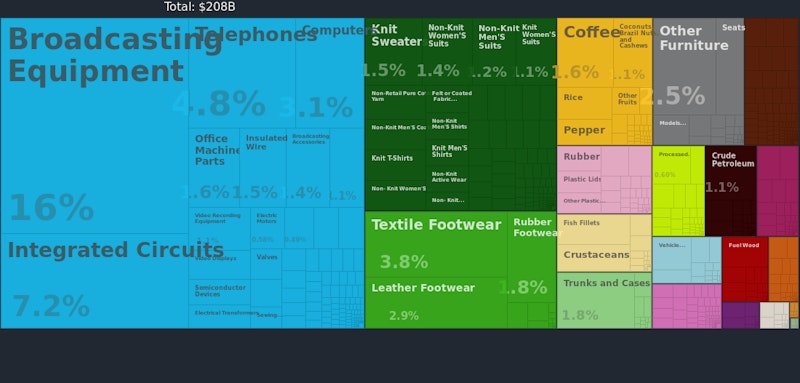
The skills, technologies and knowhow that can be used to manufacture cars might be applied to making other vehicles. The capability of processing foods might be transferred to stimulating a restaurant industry attractive to tourists. Industries are linked and richer, advanced nations develop increased economic complexity that allow them to produce and export higher valued added products embedded with deeper knowhow across the world.
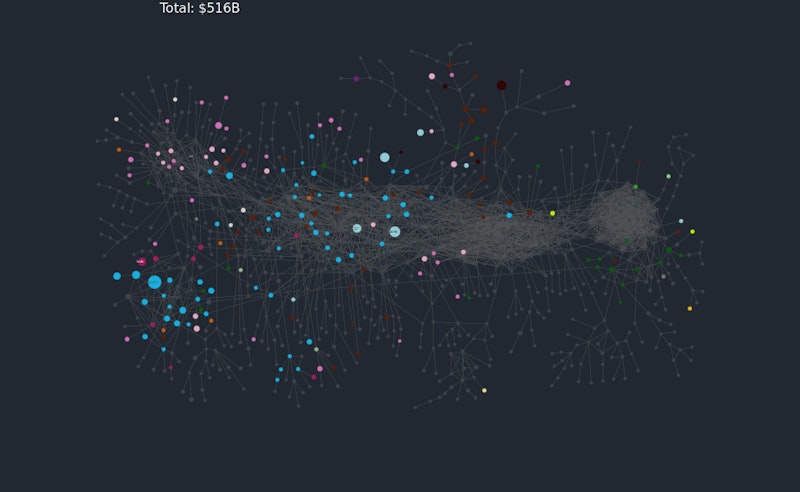
Product space map - an indicator of economic complexity
The product space is a network connecting products that are likely to be co-exported and can be used to predict the evolution of a country’s export structure.
Product space map for Germany

Germany has one of the highest levels of economic complexity in the world. Indeed the data suggests that Germany exports over 500 different products across many industries in which it has a revealed comparative advantage. Human capital is highly developed, German businesses have the capabilities to design, test, manufacture and sell a vast array of different products many of which are highly complex in industries such as bio-science, precision engineering, household appliances and much more.
Product space map for Saudi Arabia

In contrast, the product space map for Saudi Arabia shows fewer interconnections between industries. One of this country’s biggest challenges going forward is to become less dependent on oil and gas and invest in emerging industries that make different use of the nation’s human capital. Diversification is an important strand of sustainable development.
Here is Professor Ricardo Hausmann discussing the importance of know how in determining a country's competitiveness in global markets
What is the product space?
Countries can make significant progress in economic complexity over time. In 1980, South Korea was ranked 23rd on the Economic Complexity Index. The latest data finds South Korea ranked 3rd and many of you will be able to name South Korean multinational corporations with a global brand reach.
You might also like
European Single Market
Study Notes

The squeezed middle
16th August 2015

More universities generates faster growth
23rd March 2016

Under-investment by British business
11th December 2016
Zero progress in tackling school access
6th September 2017
UK Economy Update 2019: Trade & Competitiveness
Topic Videos
Vietnam - Asia's Shining Star
19th November 2020

Building Climate Resilience in Bangladesh
11th September 2022