Study Notes
Wage Rises - Income & Substitution Effects (Labour Markets)
- Level:
- A-Level, IB
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB, Eduqas, WJEC
Last updated 3 Feb 2023
This analysis looks at the individual labour supply decision and in particular the work-leisure trade off and how this is affected by a change in wages.
- Most individuals face a choice between hours worked and hours of leisure
- The opportunity cost of taking leisure is the monetary value of the wages foregone
- A change in the wage rate has both an income effect and a substitution effect
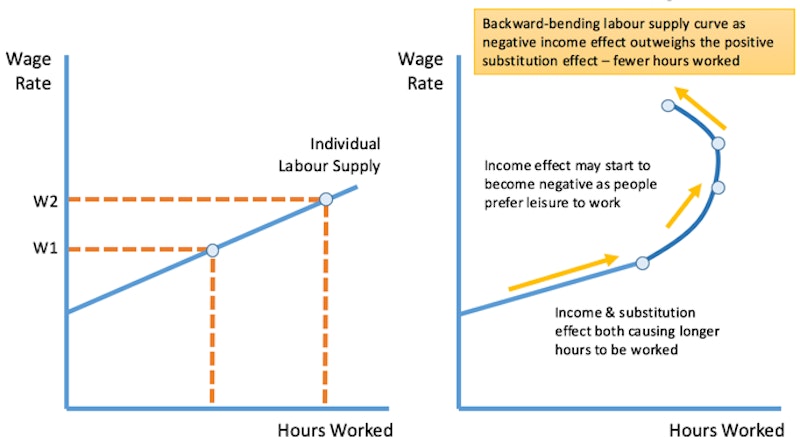
The income effect of a rise in the hourly wage rate
- Positive income effect: When higher wages cause people to want to work more hours in order to reach a target / desired income
- Negative income effect: When a target income has been reached and people prefer spending more time on leisure rather than earning more income
The substitution effect of a rise in the hourly wage rate
- A rise in the real wage increases the opportunity cost of leisure
- Therefore higher wages will always cause people to be incentivised to work longer hours via the substitution effect
- But the income effect may work in the opposite direction

Some people may have a backward bending individual labour supply curve – they may choose to work fewer hours when the wage rate rises (ceteris paribus)
You might also like

The Happy Band of the Self Employed
15th October 2014
The Poverty Trap- Panorama
12th October 2014

Factors of Production
13th April 2014
Labour Migration (Labour Markets)
Study Notes
Long Run Aggregate Supply
Study Notes
Supply-Side Reforms (Labour Markets)
Study Notes
What are the main factors of production?
Study Notes