Study Notes
Globalisation - Intra Industry Trade
- Level:
- A-Level
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB
Last updated 22 Mar 2021
Intra-industry trade means trade within industries
A measure of the intra-industry trade that takes place between countries is the Grubel-Lloyd (GL) index.
E.g. If a country only exports or imports good X (e.g. sugar) then the GL index for that sector is equal to 0. On the other hand, if a country imports exactly as much of good X as it exports, then its GL score for sector would be 1.
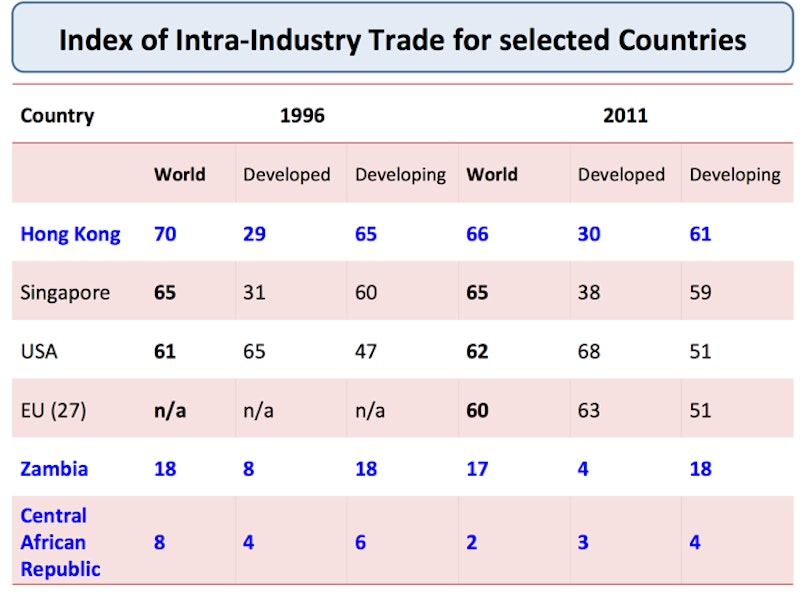
Intra-industry trade and stages of development
Developed economies and rapidly industrialising developing economies (e.g. Hong Kong, China; Singapore; Malaysia and Thailand) tend to engage in more intra-industry trade
Resource-rich developing economies and Less Developed Countries tend to have relatively little intra-industry trade
Economies such as Malaysia and Thailand have more intra-industry trade with other developing countries in the same region
Japan has more intra-industry trade with developing economies – it is net importer of commodities and it is also geographically close to several emerging "industrialized" countries such as South Korea. There is increasingly intense competition between Japanese and South Korean manufacturing conglomerate businesses
A major development theme in recent years has been for countries to build a deeper level of complexity into their economy.
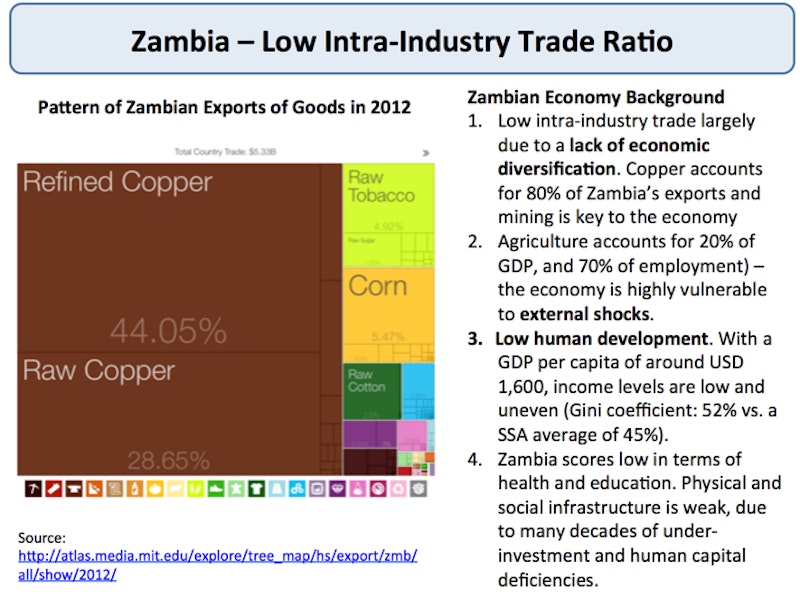
Intra-industry trade for developing countries
We observe that poor countries, even if similar in terms of income, trade much less with each other compared with rich countries
Countries where overall labour and capital productivity is low have lower wages and produce less differentiated goods and services
Many of these countries are heavily reliant on a small number of products – this gives rise to primary product dependency
Read: The Road Less Travelled – African Intra-Regional Trade – a 2013 article from the Economist: www.economist.com/blogs/baobab/2013/04/intra-african-trade
Read: Why Africa is becoming less reliant on commodities (Economist magazine, January 2015): www.economist.com/blogs/economist-explains/2015/01/economist-explains-5?fsrc=scn/tw_ec/why_africa_is_becoming_less_dependent_on_commodities
Explanations for rising intra-industry trade
You might also like

Beyond the Bike - Special Economic Zones in China and Africa
27th November 2015

What can the iPhone tell us about China's Trade?
31st May 2016
Will China rule the world?
25th January 2017
Corporate Tax Avoidance
Topic Videos
Tax avoidance costs the global economy $427bn a year,
20th November 2020

Debt Relief - Lenders urged to cancel Zambia debt
16th September 2022
4.5.4 Sovereign Wealth Funds (Edexcel A-Level Economics Teaching PowerPoint)
Teaching PowerPoints