Study Notes
GCSE Geography | Human Causes of Climate Change (Climate Change 4)
- Level:
- GCSE
- Board:
- AQA, OCR
Last updated 29 Apr 2024
Scientists have proved that natural causes, including volcanic activity, solar output and orbital changes, account for long-term climate change. However, there has been a rapid increase in warming since the 1970s, as a result of human activities that release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.

What are greenhouse gases?
Carbon dioxide
In recent years we have seen a huge increase in levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere – it accounts for about 60% of the enhanced greenhouse effect. Global concentration of CO2 has increased by 30% since 1850. Burning fossils fuels such as coal, oil and gas in industry, to generate electricity, or to power vehicles, all release huge amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere. Deforestation is also responsible – when trees are cut down to clear land for economic activity they are often burned, which gives of lots of CO2, and trees store carbon, so once they are felled this stored carbon is released back into the atmosphere.
Methane
Methane is very effective at absorbing heat and as a result accounts for 20% of the enhanced greenhouse effect and its subsequent heating of the earth. Methane is released into the atmosphere in many different ways – it is released when organic matter rots down in landfill sites or on compost heaps, it is given off when we burn biomass for energy, and one of the biggest causes is through agriculture – for example farm livestock, particularly cattle, give off methane, as does rice farming.
Nitrous oxides
These are extremely efficient at trapping heat. In fact, tiny concentrations in the atmosphere are up to 300 times more effective at capturing heat than CO2. Nitrous oxides are released into the atmosphere through lots of economic activities, such as from power stations producing electricity, released from fertilisers used to improve crop yield in farming, given off from sewage treatment plants, and are also one of the many toxins found in vehicle exhausts (and responsible for dangerous levels of air quality across thousands of global cities).
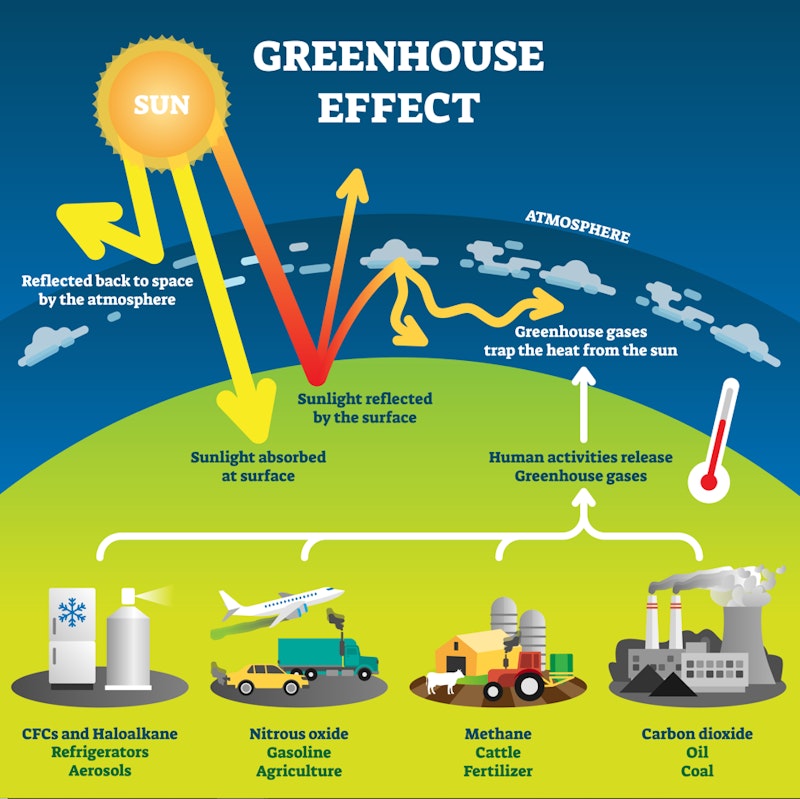
The greenhouse effect
These gases have led to a greenhouse effect - which is so called as it heats up the earth like a greenhouse.
The Sun’s infrared heat rays enter the Earth’s atmosphere - most solar radiation is able to past through it to warm up the earth’s surface – this is short-wave radiation. We call the heat given off by the earth’s surface, long-wave radiation.
Many human activities cause greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane to be released into the atmosphere – these form a blanket within the atmosphere that traps this long-wave radiation heat. We do need the greenhouse effect to keep the earth warm – without it life wouldn’t exist on earth as it would be too cold (around 33 °C colder). However what we now have an enhanced greenhouse effect where too much heat is being trapped in, leading to climate change.
You might also like

Cosmetic Firms Clean Up Their Act to Reduce Ocean Pollution
31st October 2015

Flint - The City Poisoned by its Water Supply
24th January 2016
Is our recent heatwave linked to climate change?
4th July 2017
Climate change resistant wheat crops
21st August 2018
The USA pledges to cut carbon emissions
24th April 2021
Oil and gas fields producing methane
5th February 2022

Does it Matter that COP27 is in Africa?
12th October 2022